Introduction India’s textiles sector is one of the oldest industries in the Indian economy, dating back to several centuries. The industry is extremely varied, with hand-spun and hand-woven textiles sectors at one end of the spectrum, while the capital-intensive sophisticated mills sector on the other end. The decentralised power looms/ hosiery and knitting sector […]
February 4, 2021
 Introduction
IntroductionIndia’s textiles sector is one of the oldest industries in the Indian economy, dating back to several centuries.
The industry is extremely varied, with hand-spun and hand-woven textiles sectors at one end of the spectrum, while the capital-intensive sophisticated mills sector on the other end. The decentralised power looms/ hosiery and knitting sector forms the largest component in the textiles sector. The close linkage of textiles industry to agriculture (for raw materials such as cotton) and the ancient culture and traditions of the country in terms of textiles makes it unique in comparison to other industries in the country. India’s textiles industry has a capacity to produce wide variety of products suitable for different market segments, both within India and across the world.
Textile design comprises both surface design and structural design and textile designers usually handle embroidery designs, print, weave and texture.
The courses focus on elementary ergonomics, textile fibers, color, composition, and basic textile design for weaving and printing. They also teach dyeing techniques, printing methods, sewing techniques, and construction of fabrics and surface design. These programs helps one understand all the intricacies of production, in order to find innovative solutions.
Textile designers work in garment manufacturing companies, fashion designing agencies, textile manufacturers, retail world, export houses or work as freelancers.
The textile and apparel industry is one of the earliest industries to have developed in India. Its inherent and unique strength is its incomparable employment potential owing to the presence of the entire value chain from fibre to apparel manufacturing within the country. It is the biggest employer after agriculture and provides direct employment to 4.5 crore people and another 6 crores in allied sectors. India needs to generate jobs that pay well, provide social protection to workers, support efficient production for export markets, and hold the potential for social transformation. The textile industry meets all these criteria.
India is the second-largest manufacturer of textiles and clothing in the world. India is also the second-largest exporter of textiles and apparel with a share of 5% of global trade. Exports of textile and clothing products, including handicrafts, from India have slightly increased to US$ 40.4 billion during the year 2018–19 from US$ 39.2 billion during 2017–18, registering a growth of 3%. However, India’s global share is way behind that of China, which has approximately 38% of the global textile and clothing trade. The share of textile and clothing in India’s total exports stood at 12% in 2018–19. With 48% total textile and apparel export, EU-28 and the United States are India’s major textile and apparel export destinations.
India has a very strong raw material base both in natural and manmade fibres (MMFs). India has emerged as the largest producer of cotton in the world with a production of 370 lakh bales in 2017–18 and the second-largest exporter of cotton. However, high contamination level and poor quality of fibre, both in fineness and length, are major concerns that need focused attention.
India has a strong presence in global exports of cotton yarn. Vietnam has increased its global export share of cotton yarn from 5% in 2012 to 15% in 2016. China and Bangladesh are the largest importers of cotton yarn from India, who in turn creates value addition to the yarn and then exports the same at a lower cost compared to India. India needs to upgrade its position from a supplier of cotton yarn to a producer of value-added fabrics and garments. As the world export value of cotton yarn has decreased over the years, it is an indication that the cotton textile trade is shifting towards different types of fibre such as MMF.
 While India leads in cotton yarn exports, it has been a very marginal player when it comes to cotton fabric in world exports. China has a substantial share of 51% in cotton fabrics when compared to India’s 5%–6%; the situation is almost the same in case of MMF fabrics. This comparison suggests that India is not able to scale up the value chain significantly enough to meet the global demand despite being the largest producer and exporter of cotton yarn.
While India leads in cotton yarn exports, it has been a very marginal player when it comes to cotton fabric in world exports. China has a substantial share of 51% in cotton fabrics when compared to India’s 5%–6%; the situation is almost the same in case of MMF fabrics. This comparison suggests that India is not able to scale up the value chain significantly enough to meet the global demand despite being the largest producer and exporter of cotton yarn.
Approximately 95% of the weaving sector in India is unorganized in nature. The decentralized power loom and hosiery sector contributes 85% of total fabric production. The processing segment is also dominated by a large number of independent, small-scale enterprises. Since, the weaving/processing sector in India is dominated by small-scale enterprises, it has challenges such as inadequate know-how, low focus on research, innovation in new product development and low technology upgradation. Further, low productivity and automation levels also remain one of the biggest woes for the weaving industry. Due to these factors, the overall performance of fabric production in India is getting dampened. The weaving sector still remains one of the weakest links of the Indian textile and apparel industry.
India has one of the largest installed production bases in the world in weaving sector but at the same time it uses old technology with low productivity and quality levels. In terms of technology adoption in the weaving sector, India has only 2% share in global shuttle-less looms (i.e. modern looms) installed capacity. The cost of production in India also goes up due to poor technology levels and low scale of operations, as 95% of the weaving sector in India is unorganized and in small scale. India also lacks the presence of large fabric manufacturers when compared to China and the US.
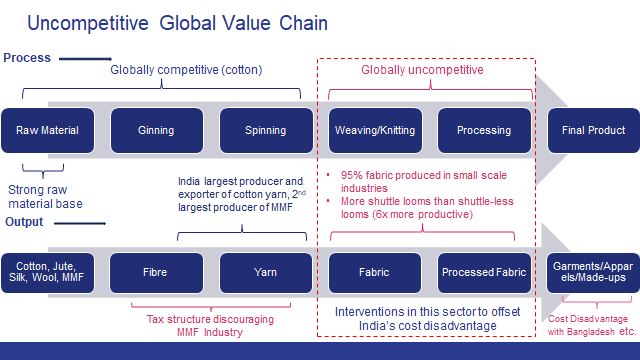
In order to make the textile industry competitive, industry needs to focus on investing in technology upgradation and expand weaving capacity to scale-up operations. To ensure rapid transformation of the weaving sector in India, under Amended Technology Upgradation Funds Scheme (ATUFS) of the Government of India, the weaving sector may be considered to get capital subsidy at par with garmenting and technical textiles. At present, the weaving sector is getting subsidy at 10% subject to cap of 20 crore under ATUFS, whereas for garmenting and technical textiles, subsidy is provided at 15% subject to cap of 30 crore. For creating few global champions in weaving sector in India, the Government of India may consider providing some enhanced subsidy under ATUFS, for select players, purely on outcome basis. Further, state governments should aggressively promote infrastructure and provide plug and play parks for the industry. Lands should be allotted in such parks for long-term lease. The supply of uninterrupted quality power at fixed price for a tenure of 15 years may also be considered in these parks. To ensure rapid scaling up of business, state governments should provide all the approvals in place, including the provision of CETPs/ZLD, as per need basis, in these parks.
The weaving sector is the backbone of the textile industry. On the one hand, promoting the weaving industry gives impetus to the domestic spinning industry and on the other, it makes our garment’ sector globally more competitive. With focused interventions in this sector, we might enhance its performance in terms of more investment, employment generation and export earnings.
 Market Size
Market SizeIndia’s textiles industry contributed 13% of the industry production in FY20. It contributed 2.3% to the GDP of India and employed more than 45 million people in FY20. The sector contributed 12% to India’s export earnings in FY20.
Textiles industry has around 4.5 crore employed workers including 35.22 lakh handloom workers across the country.
Cotton production in India is estimated to have reached 35.7 million bales in FY20.
The domestic textiles and apparel market stood at an estimated US$ 100 billion in FY19.
The production of raw cotton in India is estimated to have reached 36.04 million bales in FY20^. During FY19, production of fibre in India stood at 1.44 million tonnes (MT) and reached 1.60 MT in FY20 (till January 2020), while that for yarn, the production stood at 4,762 million kgs during same period.
The textiles sector has witnessed a spurt in investment during the last five years. The industry (including dyed and printed) attracted Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) worth US$ 3.45 billion from April 2000 to June 2020.
Indian government has come up with several export promotion policies for the textiles sector. It has also allowed 100% FDI in the sector under the automatic route.
Following are the achievements of the Government in the past four years:
The future for the Indian textiles industry looks promising, buoyed by strong domestic consumption as well as export demand. With consumerism and disposable income on the rise, the retail sector has experienced a rapid growth in the past decade with the entry of several international players like Marks & Spencer, Guess and Next into the Indian market.
High economic growth has resulted in higher disposable income. This has led to rise in demand for products creating a huge domestic market.
Address:- 2nd Floor, F 18, Gautam Marg, Vaishali Nagar, Jaipur, Rajasthan -302021
Contact Person: Mr. Aman and Mr. Akbar
Contact No: 97721-99911, 0141-6656509
Email: jaipur@pahaldesign.com